1. Clausena anisata (Horsewood)
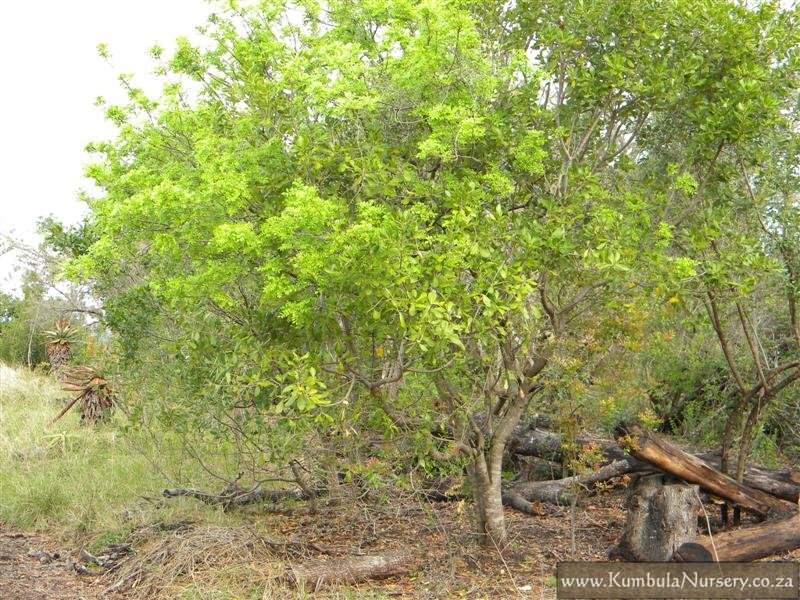
Clausena anisata (Size 3 to 10m) is a very hardy, evergreen, shrub or small tree that is spindly when young but matures to a lovely rounded shape. It bears sprays of attractive creamy-white flowers from May to August. These are followed by black berries that attract birds to the garden. The attractive compound, glossy leaves droop gracefully. When crushed they emit a strong smell and can be used as a substitute for curry leaves. It is the host plant of several Swallowtail butterflies. Plant in sun or semi shade. It makes an ideal specimen tree for a small garden. It has many medicinal and magical. (Information from Random Harvest) Some of these uses include
Clausena anisata (Image from KumbalaNursery.co.za)
2. Moringa oleifera (Moringa)
The small fast-growing and hardy Moringa oleifera tree is also known as the drumstick tree, horseradish, been oil tree or ‘peperwortelboom’ in Afrikaans. Growing between 5 and 12 m tall, it has a straight trunk and and umbrella-shaped crown of feathery green leaves. Flowers are up to 25 cm long and produce thin and long reddish brown seed pods. Although native to India, Pakistan and Nepal, Moringa oleifera grows in the Limpopo, Free State, Mpumalanga, KwaZulu-Natal and Gauteng provinces of South Africa.
According to traditional African and Indian (Ayurvedic) medicine moringa has almost 540 compounds that can treat or prevent about 300 health issues. Used for centuries in Eastern countries for diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, anemia, arthritis, liver disease, as well as respiratory, skin and digestive disorders, it is now considered a ‘super-food’. The powdered leaves, roots, bark and immature pods are used for its nutritional, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and tissue-protective benefits.
Moringa is a source of vitamins, minerals, as well as all the essential amino acids, making it a complete protein. It contains significant amounts of vitamin C, E, potassium (K), iron (Fe) and zinc (Zn). In addition moringa leaves are an excellent calcium (Ca) source and contain 10 times more vitamin A (beta carotene) than carrots. moringa powder can be used as a substitute for iron tablets, hence as a treatment for anemia. Beef has only 2 mg of iron while moringa leaf powder has 28 mg of iron.
In India, moringa leaves are used stimulate breast milk production in new mothers and usually added to lentil soups during the cold and flu season to increase disease resistance. The leaves, gums, roots, flowers as well as kernels have been utilized for managing tissue tenderness, cardiovascular and liver maladies, normalize blood glucose and cholesterol. It has also profound antimicrobial and anti-TB activities.
In developing countries, the moringa leaf powder is commonly used as a medicinal herb, rather than food as in Asian populations. It is often taken as a supplement by HIV-infected people to enhance immunity and manage opportunistic infections. The fact that moringa is easily cultivable makes it a sustainable remedy for malnutrition - countries like Senegal and Benin treat children with moringa. Moringa products range from leaf extract, powder and tablets to protein shakes, seed oils, teas and probiotic drinks. Leaves can be harvested by cutting the top of the plant off when the plant has grown to 1 m, leaving about 30 cm. It is easily propagated by seeds, but needs nitrogen for good yields. It prefers daily temperatures of 25 to 30 °C and neutral, well-drained soils, but can grow well in clay soils. (http://southafrica.co.za/moringa-miracle-medicine.html)
Moringa Tree (Image from https://www.seedsforafrica.co.za/products/moringa-oleifera-tree-medicinal-seeds)
3. Tarchonanthus camphoratus (Camphor Bush)
Tarchonanthus camphoratus is a hardy, large, decorative, evergreen shrub or small tree with attractive silver foliage that smells of camphor when crushed. Sprays of white, thistle like flowers covered in white woolly hairs are borne from March to November. All parts of the plant are aromatic and smell strongly of camphor. This useful plant makes an excellent screen and windbreak. It has a fibrous root system and can be used for binding the soil. It also makes a lovely shade tree for a small garden. This drought resistant shrub is heavily browsed on by game. Used extensively as a medicinal plant.The wood is beautiful and among other things has been used to make musical instruments. Grows Up to 5m (Information from Random Harvest)
The camphor bush is used for medicinal purposes. Problems such as blocked sinuses and headache can be healed by inhaling the smoke from the burning green leaves. Drinking boiled mixture of leaves and water can help to treat coughing, toothache, abdominal pain and bronchitis. Leaves can also be used for massaging body stiffness and also as a perfume. The cotton wool-like seedheads were used to stuff cushions. (http://pza.sanbi.org/tarchonanthus-camphoratus)
Camphor Bush (Image from http://pza.sanbi.org/tarchonanthus-camphoratus)
4. Warburgia salutaris (PepperBark Tree)
The endangered pepper-bark tree of southeastern Africa, Warburgia salutarus, grows in South Africa, Swaziland, Mozambique and Zimbabwe. The name ‘salutaris’ means health giving, alluding to the pepper-bark’s medicinal uses. A related species, known as ‘Karambaki’, has been used medicinally by Arab traders, East African residents since ancient times. Pepper-bark is extremely rare to find in the wild and is listed as a Red Data Book threatened species. Heavy harvested by traditional healers for its much sought-after bark used in traditional medicine, considerable effort is made to encourage propagation of this tree.
It grows easily from cuttings or root suckers in well-drained soil rich in organic matter and makes an attractive landscaping plant. A tropical tree, the slender evergreen pepper-bark grows 5-10m tall and fixes nitrogen in the soil while its leaves makes an nitrogen-rich mulch. Small yellow-green flowers form 30 mm round berries that ripen to a purple colour. Leaves, fruit and inner bark have a strong peppery taste and harvesting is severely impeded by the fruit’s popularity with fruit flies and monkeys. The trees are slow to mature and can only be harvested at around 10 years old, but takes 20 years to reach full maturity.
The bark and leaves of the pepper-bark contain various compounds with antibacterial, anti-fungicidal (particularly against Candida yeast infections), anti-ulcer and diuretic properties. The plant material is dried, then crushed into a powder and used as infusions and decoctions to treat vaginal thrush, chest infections, venereal diseases, body aches, stomach problems (diarrhoea, aches) and malaria. Used as a snuff, it clears nasal passages and when the bark is chewed or the smoke inhaled, it remedies chest complaints, relieves constipation, fevers and body pains. An infusion of the leaves helps against rheumatism and skin diseases, while boiled roots are added to soup to cure diarrhoea. Both stems and root bark are remedies for malaria and when ground up and mixed with water, it can cure mouth sores. In Kenya, the leaves are added to flavour curries. (http://southafrica.co.za/pepperbark-tree-endangered-medicine-plant.html)
Image from http://pza.sanbi.org/warburgia-salutaris
5. Lannea discolor (Live Long)
Lannea discolor is a small to medium-sized deciduous tree with a neat round crown occurring in bushveld. It is often found on rocky granite ridges. The tree grape is a medium-sized deciduous tree that grows up to 15 m in height with a neat rounded crown. Lannea discolor is generally used as traditional medicine to treat fevers and constipation in children. Its fruits are edible and are utilized by animals, birds and humans. The wood is soft and used to make fences. Fencing poles made out of the wood will easily take root and flourish again, which has earned it its common name Live long. (http://pza.sanbi.org/lannea-discolor)
Lannea discolor (http://pza.sanbi.org/lannea-discolor)